News
A scientific knowledge base relating digital writing tools for future education from interdisciplinary perspectives
The scientific knowledge base is a synopsis of 158 international scientific sources (book chapters, original articles, reviews, and reports):
These sources were synthesized into a scientific knowledge base corresponding to the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Handwriting is important for education and needs to be preserved.
Hypothesis 2: There are problems connected with handwriting in the educational context, and handwriting is transforming.
Hypothesis 3: Digital writing tools could support handwriting transformation processes and offer solutions to associated problems.
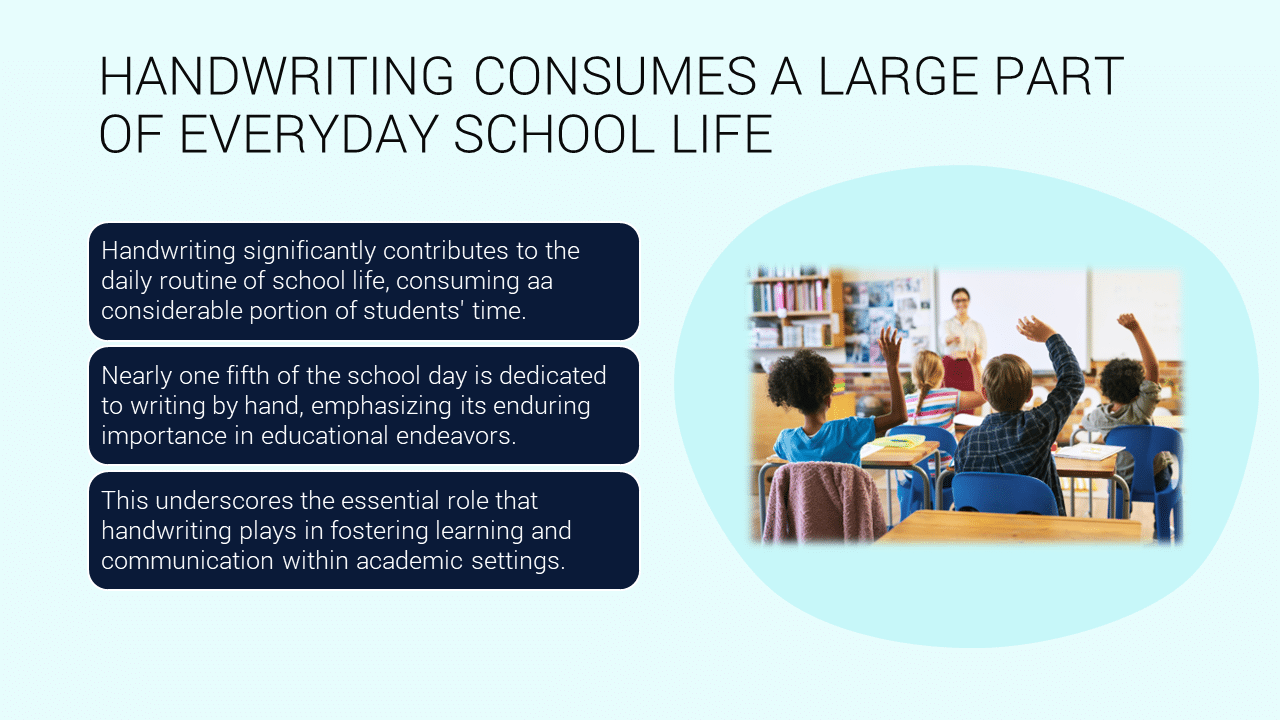
Handwriting is an integral part of the school day, playing a crucial role in students’ educational experience. On average, nearly one fifth of the school day is dedicated to writing by hand, highlighting its significance in fostering learning and communication. This considerable time investment underscores the importance of handwriting in developing essential skills, from fine motor abilities to cognitive functions. As students engage in various writing activities, they enhance their capacity for expression and comprehension, making handwriting a fundamental component of effective education.
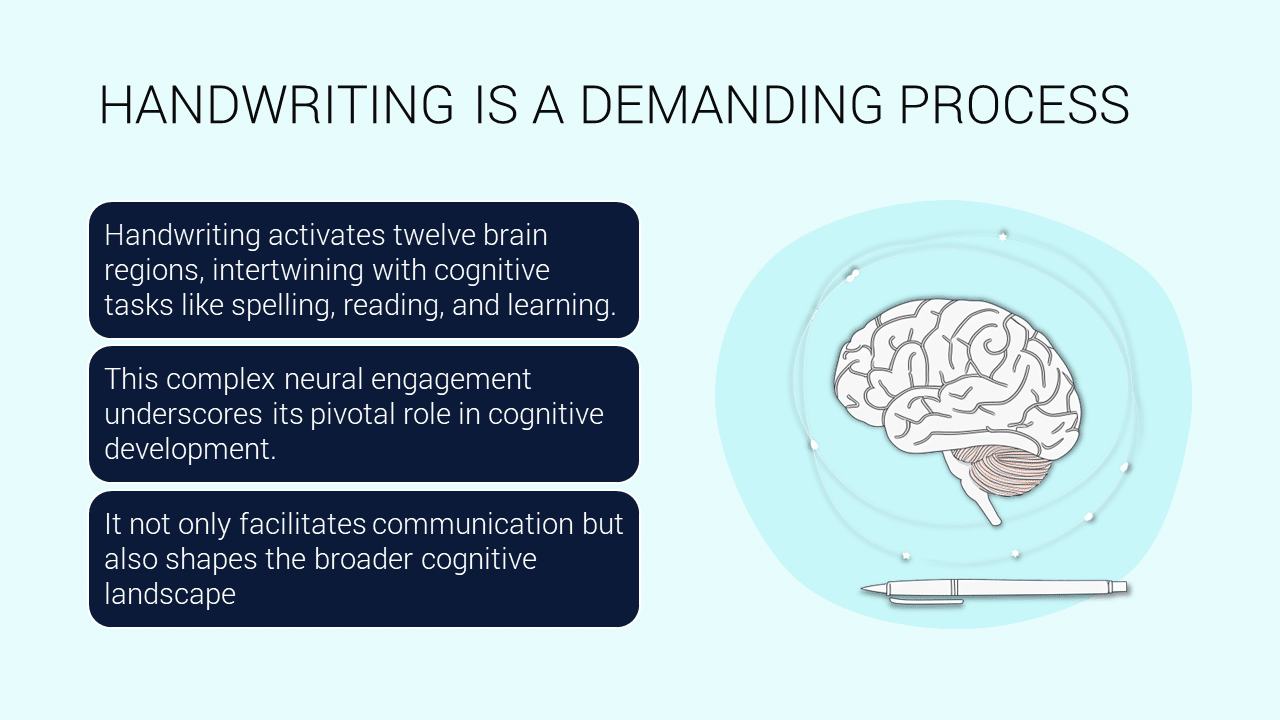
Handwriting is a demanding process that activates twelve distinct brain regions, intertwining with essential tasks such as spelling, reading, and learning. This extensive neural engagement underscores the role of handwriting in cognitive development, and shows how deeply it influences the functioning of the brain. Beyond just facilitating effective communication, handwriting plays a significant role in shaping the broader cognitive landscape and impacting how we process, retain, and understand information. The relationship between handwriting and brain activity highlights its value in educational settings and its impact on lifelong learning and cognitive abilities.

The distinctiveness of handwriting makes it a powerful tool in forensic authentication, offering valuable insights into individual identity. Each person’s unique nuances and personal characteristics in their handwriting assist experts in verifying documents and signatures, ensuring the accuracy and authenticity of important records. This individuality of handwriting helps in understanding historical documents, making it an indispensable resource in both legal and historical contexts.

Handwriting is intricately linked with academic success, serving as a fundamental skill that impacts various aspects of students’ lives. Beyond its academic implications, proficient handwriting is associated with enhanced cognitive abilities, bolstering psychological and social well-being across all age groups. This interconnected relationship underscores the importance of handwriting in fostering overall student development and success. By preserving and emphasizing the practice of handwriting in education, we ensure that students benefit from its extensive cognitive, psychological, and social advantages, laying a strong foundation for their future achievements.

Symptoms of handwriting problems can be categorized into two main groups: those indicative of underlying physiological and cognitive processes, and those pertaining to the quality of the final output. This division highlights the multifaceted nature of handwriting difficulties, which can arise from both internal cognitive functions and external manifestations in the form of written expression. Understanding these categories is crucial for identifying and addressing the root causes of handwriting issues, ensuring that interventions can be tailored to improve both the cognitive processes and the quality of written work.
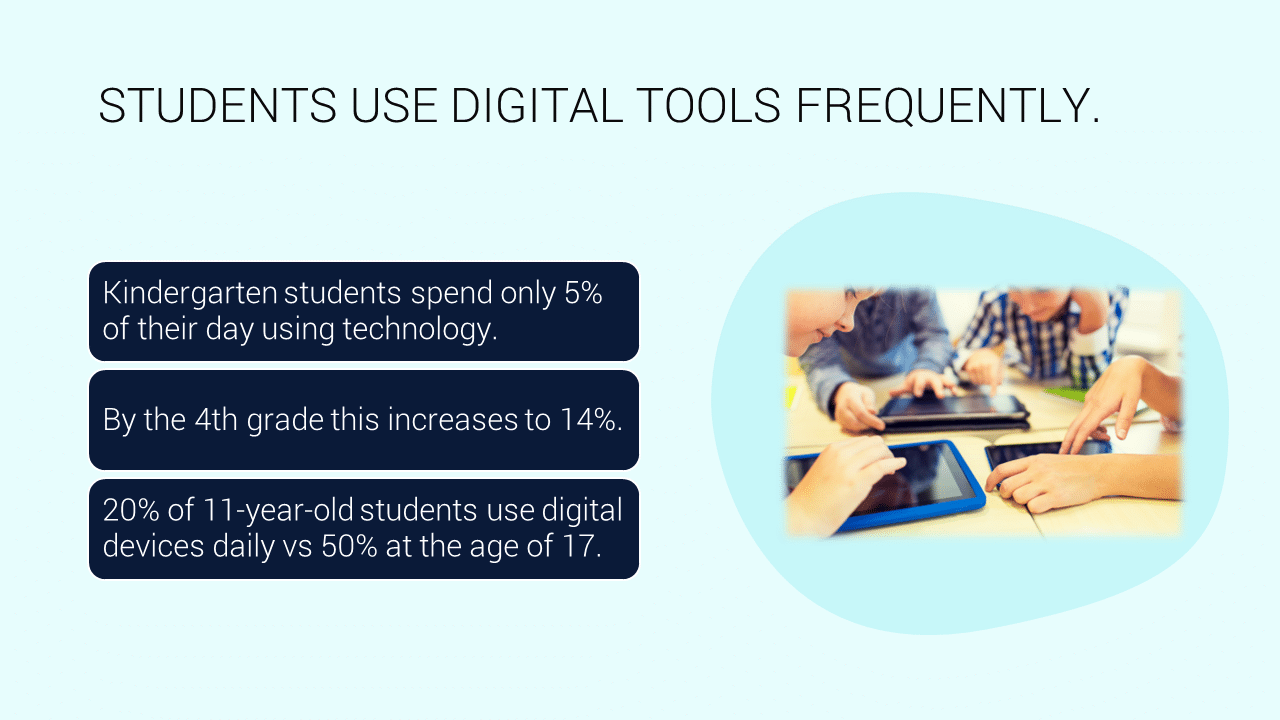
Kindergarten students spend only 5% of their day using technology. By the 4th grade, this increases to 14%. Furthermore, 20% of 11-year-old students use digital devices daily, a figure that rises significantly to 50% by the age of 17. These statistics illustrate the growing reliance on digital tools as students progress through their education, highlighting the importance of balancing traditional skills like handwriting with digital proficiency.
There are numerous advantages and added values to using digital writing tools in education. These include motivating students by making the learning process more engaging and interactive, and facilitating collaborative working by allowing students to seamlessly work together on projects and assignments. Digital writing tools also promote the inclusion of specific groups by supporting the needs of diverse learners, thus enhancing inclusivity. Additionally, these tools increase digital competence, better preparing students for future challenges in a technology-driven world. From a sustainability perspective, digital writing reduces the need for paper, contributing to environmental conservation. Furthermore, digital writing tools make it easier to edit and revise texts, improving the quality of students’ written work. These benefits underscore the significant role that digital writing tools play in modern education, offering a range of advantages that support both learning and sustainability.

On the opposite side, there are several disadvantages and risks associated with students using digital writing tools. These include the loss of haptics, which refers to the tactile feedback and fine motor skills developed through traditional handwriting. Technical problems can also disrupt the learning process, and the higher costs of digital devices and software may be a barrier for some schools and families. Additionally, digital tools can create distractions in class, potentially detracting from the learning experience. The loss of personal touch is another concern, as digital writing can feel less personal and engaging compared to handwritten notes. Furthermore, students may miss out on the cognitive and developmental advantages associated with handwriting. Health hazards, such as strain on the eyes and back muscles from prolonged use of digital devices, are also significant concerns.
Despite these challenges, there is still unexhausted potential when incorporating digital writing tools in education. These tools can support individual learning and inclusion, address the specific needs of different age groups, and prepare digital solutions for future education. By carefully balancing the use of digital and traditional writing methods, educators can maximize the benefits while mitigating the risks.
If you’re eager to explore this topic further and gain full access to our comprehensive scientific knowledge base, don’t hesitate to reach out to us today!
